Osteochondrosis is a progressive degenerative change that affects the intervertebral discs. The pathology can appear in any part of the spine, but most frequently affects the cervical spine.
The problem cannot be neglected, because over time the symptoms increase and the pathology itself can lead to serious health problems.
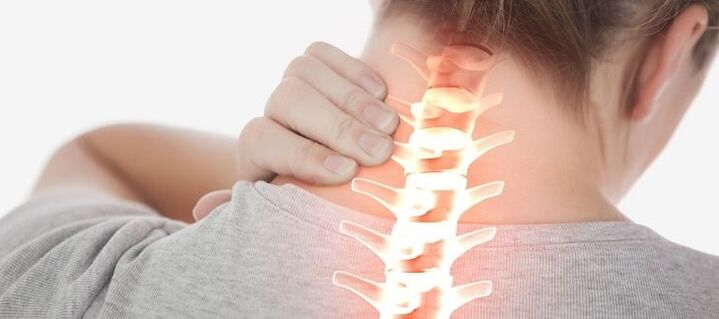
What is
The human spine consists of individual vertebrae, between which there is a specific spacer - the intervertebral disc. It is made up of cartilaginous tissue and acts as a shock absorber, protecting the bone tissue of the vertebra from abrasion and destruction, but at the same time it flattens and wears out.
Normally, these processes occur along with the aging of the human body and begin no earlier than 50-55 years. But every year the pathology becomes younger, cases of premature wear of cartilage tissue have been recorded even in young people (25-30 years old).
The high percentage of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine in comparison, for example, with the lumbar spine, is associated with loads on this particular part, caused by the need to keep the skull in an upright position.
The weight of the head of an adult can reach 3-5 kg: the weight of the bones of the skull is about 1400 g, about the same weight is that of the brain, about 500 g is the mass of blood circulating in the skull.
A feature of the cervical spine is the closer location of the vertebrae to each other and the smaller thickness of the intervertebral discs, which causes complications even with minor changes in them.
Reasons for development
Factors contributing to the development of pathological changes in cartilage tissue:
- sedentary lifestyle;
- forced tense postures during work (driving, in front of the computer);
- over weight;
- state of nervous tension;
- neck injuries;
- muscular weakness.
The muscles in the neck try to compensate for the load caused by these factors, causing spasms. Blood circulation, nutrition of cartilage tissue and metabolic processes are disturbed, which leads to a change in its structure.
Premature aging of intervertebral discs is also influenced by:
- hereditary predisposition;
- autoimmune diseases that cause degeneration of cartilage tissue;
- congenital pathologies of spinal development.
Stages and symptoms of the development of pathology.
Degenerative changes go through several stages, which are accompanied by specific symptoms:
Level 1. The symptoms remain practically invisible. At this stage, it is possible to stop or slow down the pathological process without the help of medications (diet, exercise). The patient may feel:
- discomfort in the muscles of the neck and shoulders, their tension, hardness;
- mild pain when turning or tilting the head;
- headaches that occur infrequently and are of low intensity (appear most often after static or strenuous work, nervous experiences).
Stage 2. The height of the intervertebral discs decreases, compression of the nerve endings occurs, which is why intense pain appears in the neck, especially when performing movements and turns. Muscle spasm interrupts the blood supply to the skull, thereby adding to the symptoms associated with vascular insufficiency. The person notices:
- cracking in the neck joints when turning the head;
- Decreased visual acuity;
- tinnitus;
- dizziness;
- frequent headaches for no apparent reason;
- numbness of the face and neck, loss of sensitivity in the skin of the hands and in the cervical neck area;
- shooting pains radiating to the shoulder blade;
- sleep disorders.
Stage 3. A herniated disc forms (its nucleus protrudes into the spinal canal), which causes alterations in the functioning of the nervous system. Symptoms may include:
- numbness of the hands, possible paralysis of the upper extremities;
- the pain affects the entire cervical collar area and can radiate to the heart area;
- "floaters" appear in the eyes, nausea and vomiting;
- feeling of a lump in the throat or pain, such as a sore throat;
- the skin on the upper body may not be felt at all;
- dizziness occurs with almost any movement;
- Headaches are migraines in nature.
Stage 4. Characterized by complete destruction of the disk:
- tinnitus can be permanent;
- dizziness may be accompanied by loss of consciousness;
- Coordination disturbances appear as blood supply to the cerebellar region of the brain is reduced.
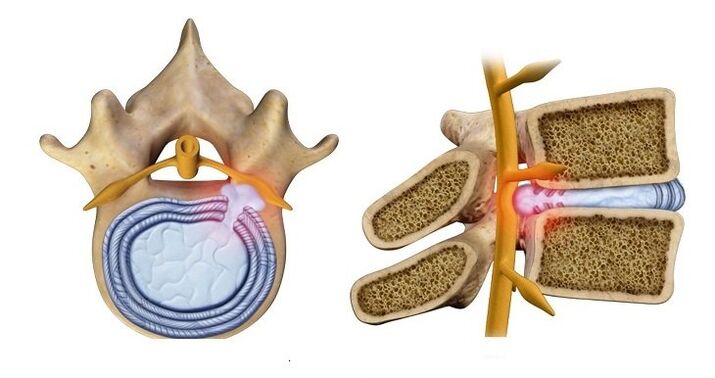
Single intervertebral discs are very rarely affected. Normally the process involves the entire department. The destruction of individual discs can occur in different stages.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of cervical osteochondrosis includes instrumental examinations and evaluation of the symptom complex.
Of the instrumental methods, the main information will be provided by:
- x-ray - will show changes in the structure of the spine, but in advanced stages of the pathology;
- CT scan - shows changes in the vertebrae, but intervertebral hernias and spinal cord compression are difficult to distinguish;
- magnetic resonance imaging - allows you to see intervertebral hernias and the direction of their growth;
- Duplex ultrasound scan - shows the speed of blood flow in the area where osteochondrosis is suspected.
When making a diagnosis, the doctor is based on the syndrome that manifests itself in the patient. A syndrome is a combination of symptoms of a disorder.
With cervical osteochondrosis, the following syndromes can develop:
vertebral- indicates that the pathological process involves bone and cartilage tissue. Manifestos:
- limited neck mobility;
- pain when turning the neck;
- structural changes in the vertebra or intervertebral disc (shown by x-ray).
Vertebral artery syndrome– means that the vertebral artery, which supplies blood to the brain, is involved in the pathological process. Main symptoms:
due to lack of blood flow:
- noise in the ears;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sudden increases in pressure;
due to irritation of the nerve endings of the artery:
- severe headache (migraine);
- numbness of the skin of the scalp;
- "floaters" in the eyes or temporary blindness;
due to lack of oxygen;
- Fainting;
- lethargy;
- loss of the ability to concentrate on anything;
- depression;
- panic attacks.
Cardiac.Signs similar to problems with the cardiovascular system:
- pain in the breastbone (sometimes like a burning sensation);
- shortness of breath and fatigue;
- acceleration of heart rate.
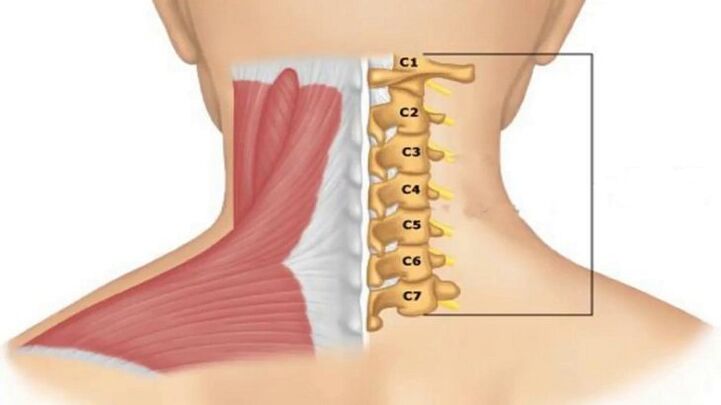
Koreshkovy.Associated with impaired conduction of nerve impulses depending on damage to a specific pair of roots innervating the cervical region:
- 1st-2nd pair of roots: pain or numbness in the back of the head;
- 3rd pair – numbness of the tongue, difficulty chewing food;
- 4th pair: pain in the collarbone, lump in the throat, difficulty swallowing food;
- 5th pair – difficulty moving the arms with the problem concentrated in the shoulder area;
- 6th pair – discomfort in the area of the shoulder blades and forearms;
- 7th pair – numbness of the hands, most often of the middle and index fingers;
- 8th pair: numbness of the ring and little fingers.
Treatment options
Only an integrated approach is applicable to the treatment of osteochondrosis. The fight against pathology can even last many years.
drug therapy
The use of drugs for cervical osteochondrosis is aimed at:
- ease the pain;
- relieve inflammation and swelling;
- reduce muscle tension in the neck area;
- improve blood circulation;
- Protect cartilage tissue from destruction and promote its restoration.
To diagnose and treat cervical osteochondrosis, you should contact a neurologist. If the clinic has a vertebrologist who directly deals with spinal diseases, you can contact him immediately.
Your doctor may prescribe the following medications:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: relieve inflammation and swelling, reduce pain.
- B vitamins: help improve the functioning of nervous tissue.
- Chondroprotectors - protect cartilage tissue from destruction and restore its structure.
- Medications that improve blood flow.
- Muscle relaxants are medications that relieve muscle spasms.
Physiotherapeutic methods.
Physiotherapy methods can quickly alleviate the patient's condition and are combined with medications:
- Electrophoresis– exposure of the affected area to low intensity electrical current. Delivers medicinal substances directly to the problem area. It is usually prescribed with an anesthetic to relieve pain or with a medication to improve blood flow to the cervical region.
- Ultrasound– has anti-inflammatory properties, improves blood flow and metabolic processes.
- Magnetotherapy– helps to quickly relieve tissue inflammation and improve metabolic processes.
- laser therapy– helps improve blood circulation at the site of exposure and also has an anti-inflammatory effect.
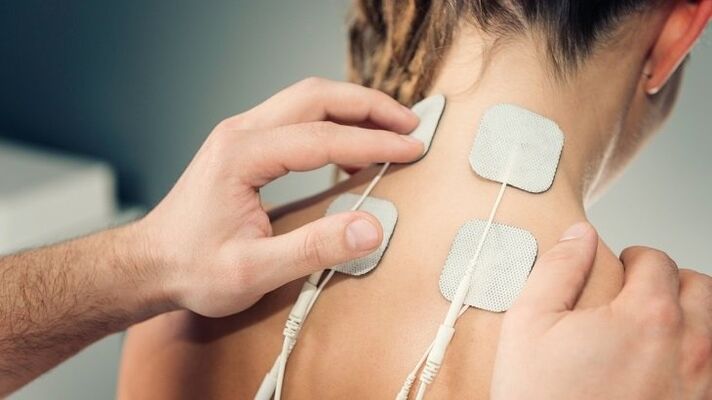
Massage
During the course of medication and physiotherapy treatment, it is better to undergo a massage in the cervical collar area by a specialist.
Self-massage can be used in the future, only very carefully, without trying to repeat the depth of impact shown by a professional masseuse.
When performing the procedure, the specialist uses classic massage techniques:
- stroking – activates the superficial layers of the skin;
- tighten – connects the deep layers of the skin;
- rubbing - warms up the muscles and relaxes them, improves blood circulation;
- kneading: affects very deep tissues, so they are used with care;
- vibration: tapping and shaking that ends the procedure.
Manual therapy
Sometimes with cervical osteochondrosis, it is recommended to consult a chiropractor. But this technique causes conflicting reviews: in some cases it certainly helps, in others it almost makes it worse. The point is this:
- There is no doubt that a chiropractor must be a highly qualified doctor with medical training and qualifications as a neurologist or orthopedic traumatologist.
- Manual therapy for cervical osteochondrosis has many contraindications. Two people with similar symptoms may receive different answers about the need for manual therapy: one can and should, the other cannot at all.
To contact a chiropractor there must be strict indications and no contraindications. They are determined by the treating doctor and give instructions for this type of therapy.
A highly qualified chiropractor will not work with a patient without studying the x-ray results.
Home treatment
Traditional treatment recipes or the use of any home remedy should be consulted in advance with the doctor, since in each specific case they can help or worsen the disease.
This applies, for example, to the needle applicator used. It consists of plastic spikes attached to a wide tape, which a person applies to the painful area (they can lie on them). The thorns cause irritation of the skin receptors and increase local blood circulation. But it cannot be used for infectious and vascular diseases.
It is also popular to warm the diseased area with mustard plaster or a bag of salt or sand. But in the case of vascular diseases this can also be dangerous.
Therapeutic exercise (physiotherapy)
Therapeutic exercises are the safest method of treating cervical osteochondrosis. It is recommended to do this both during the exacerbation and in the future to prevent the disease.
The patient should not feel pain when performing the exercises. Doing it "through pain" not only will not bring any benefit, but it can also harm your health.
The simplest but most effective movements are twists, push-ups and head rotations. It is strictly prohibited to do this at high speed and amplitude. Movements should be barely perceptible. Despite such reduced mobility, exercise guarantees blood flow and improves circulation in the neck area.
flip flop collar
The Shants collar is a rigid head support that relieves tension in the neck muscles and prevents movements that can cause pain. It is recommended to use it both during the treatment and for the prevention of cervical osteochondrosis.
The necklace is worn constantly. The vertebrae are fixed in the correct position and do not put pressure on each other, nor on blood vessels and nerve endings. As a result, pain disappears, blood circulation normalizes, and many symptoms of pathology disappear.
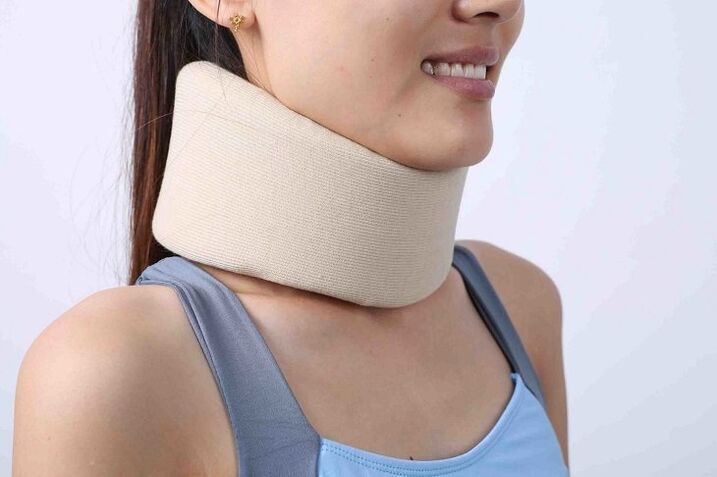

If 5-7 cervical vertebrae are unstable, a bandage cannot be used, since it will not be possible to fix it in the correct position. It is also not recommended to wear a collar if the thyroid gland is enlarged.
Application of an orthopedic pillow.
Most often, osteochondrosis is aggravated due to compression of the cervical artery and nerve roots while sleeping on an uncomfortable pillow. An orthopedic pillow guarantees a uniform horizontal position of the spine during the night.
By itself, it will not cure osteochondrosis, but it will alleviate the condition, and will also be a good measure to prevent the development of degenerative processes in the spine.
Prevention
There are simple rules that, if followed, will help prevent premature aging of the intervertebral discs:
- control your weight, exceeding the norm by 10 kg creates a critical load on the entire spine;
- try not to lift or carry heavy things;
- if you need to carry a heavy bag, hold it alternately with your right and left hand (or it is better to use a backpack that evenly distributes the load across your entire back);
- every half hour of static work should be alternated with light exercises to relieve muscle tension and improve blood circulation;
- It is useful to perform physical education exercises and sports, for example, swimming, but running, jumping and lifting weights are harmful to the spine;
- To sleep, use an orthopedic mattress and pillow.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine can significantly worsen a person's quality of life. The disease can be treated in the early stages, but even as it develops, daily performance of a series of exercises, compliance with the rules of prevention, massage and other measures prescribed by the doctor allow you to lead a comfortable life.






















